Linux adding a timestamp to the bash history
permalinkIn Linux systems, by default, the history does not include a timestamp, which can be annoying when you want to see when a command was executed to determine an update or some kind.
So today, I'll be showing you how to enable timestamps for the bash history in Linux.
Retrieving the history permalink
Before we get started, let's look at how the history works and which files are attached.
The bash history is kept so we can retrieve whatever actions some user did.
To retrieve this history, we can type the following command.
historyIt should come back with something that looks like this.
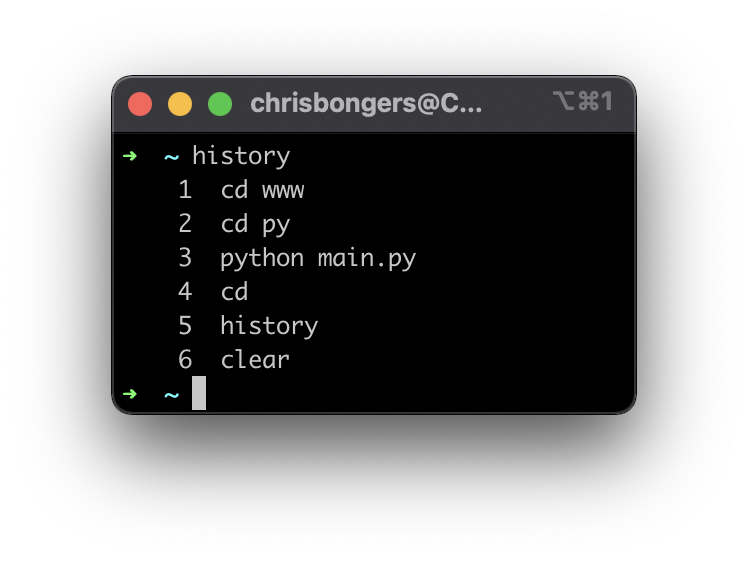
To find where this file is located you can run the following command.
echo $HISTFILEIt will generally come back with a location like:
/root/.bash_historyChanging the bash history output format permalink
However, to change the history output, we have to make a change in the configuration settings.
These configuration settings are set in a file called .bashrc.
We need to add the HISTTIMEFORMAT config settings, which will change the output.
There are two ways to include this in your .bashrc file.
- Manually open the
.bashrcfile and paste it in. - Echo it into the file.
# method 1
nano ~/.bashrc
# now paste:
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T "
# method 2
echo 'export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T "' >> ~/.bashrcThe format we are using includes the %F and %T variables which stand for:
%F: full date (year-month-day)%T: time (hour:minute:seconds)
Now you won't see the change yet. We have to enable it, which we can do by rebooting or simply running this command:
source ~/.bashrcNow when we run the history command, we should see something like this.
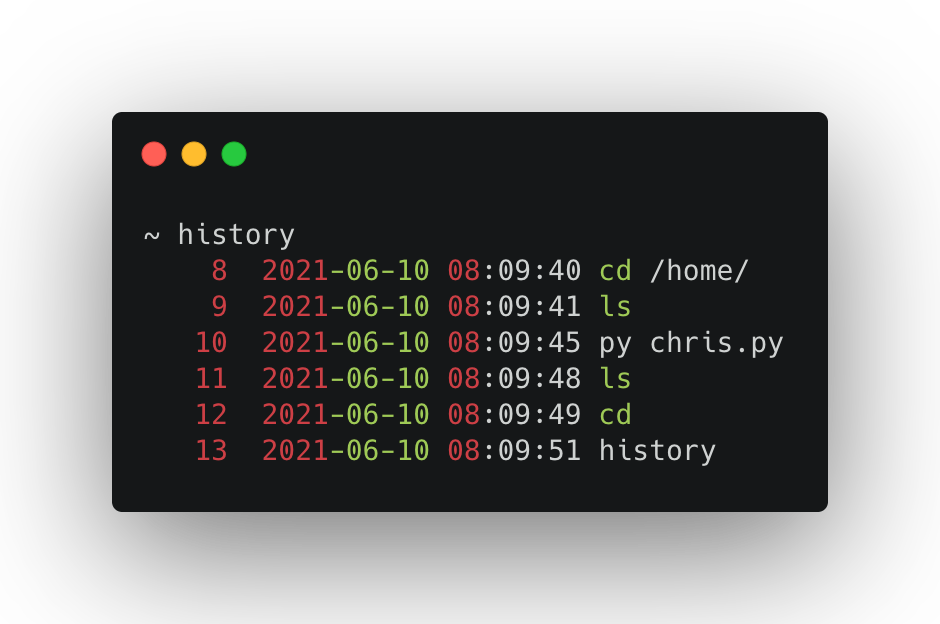
As you can see, we now have timestamps in front of our history!
Thank you for reading, and let's connect! permalink
Thank you for reading my blog. Feel free to subscribe to my email newsletter and connect on Facebook or Twitter